What’s the context?
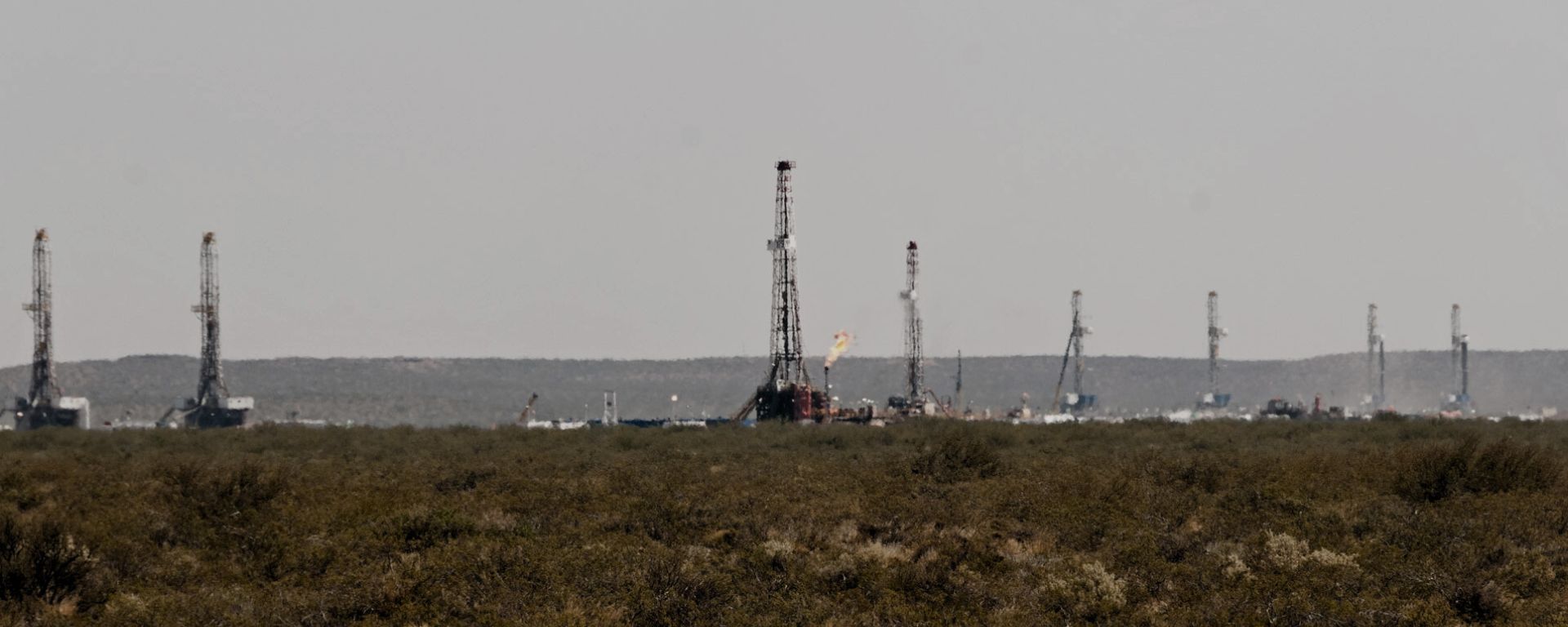
South America’s vulnerable Amazon rainforest region is a rising frontier for oil and gas drilling.
RIO DE JANEIRO – At the mouth of the Amazon River, Brazil’s most promising oil frontier is at the centre of a dispute between environmentalists and South America’s largest company.
Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva is pressuring the government’s environment agency Ibama to drop its objections to allowing state-controlled oil energy Petrobras to drill for oil in the Equatorial Margin region, off the northeast coast.
Environmental groups have been calling for a ban on fossil fuel drilling in the Amazon, where scientists say climate change has contributed to a record drought.
However, the Petrobras bid to drill near the mouth of the river is only one of many in the region, where most countries are highly reliant on fossil fuels for exports.
Here is what you need to know:
Where are fossil fuels drilled in the Amazon?
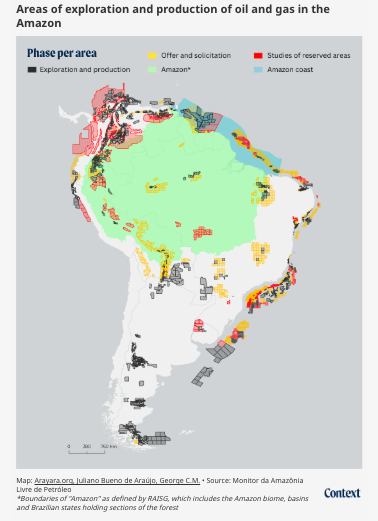
Some of the oldest fossil fuel blocks in the Amazon are located near the western limits of the Amazon basin, between southern Colombia, eastern Ecuador and northern Peru, which have been drilled for oil since the late 1960s and early 1970s.
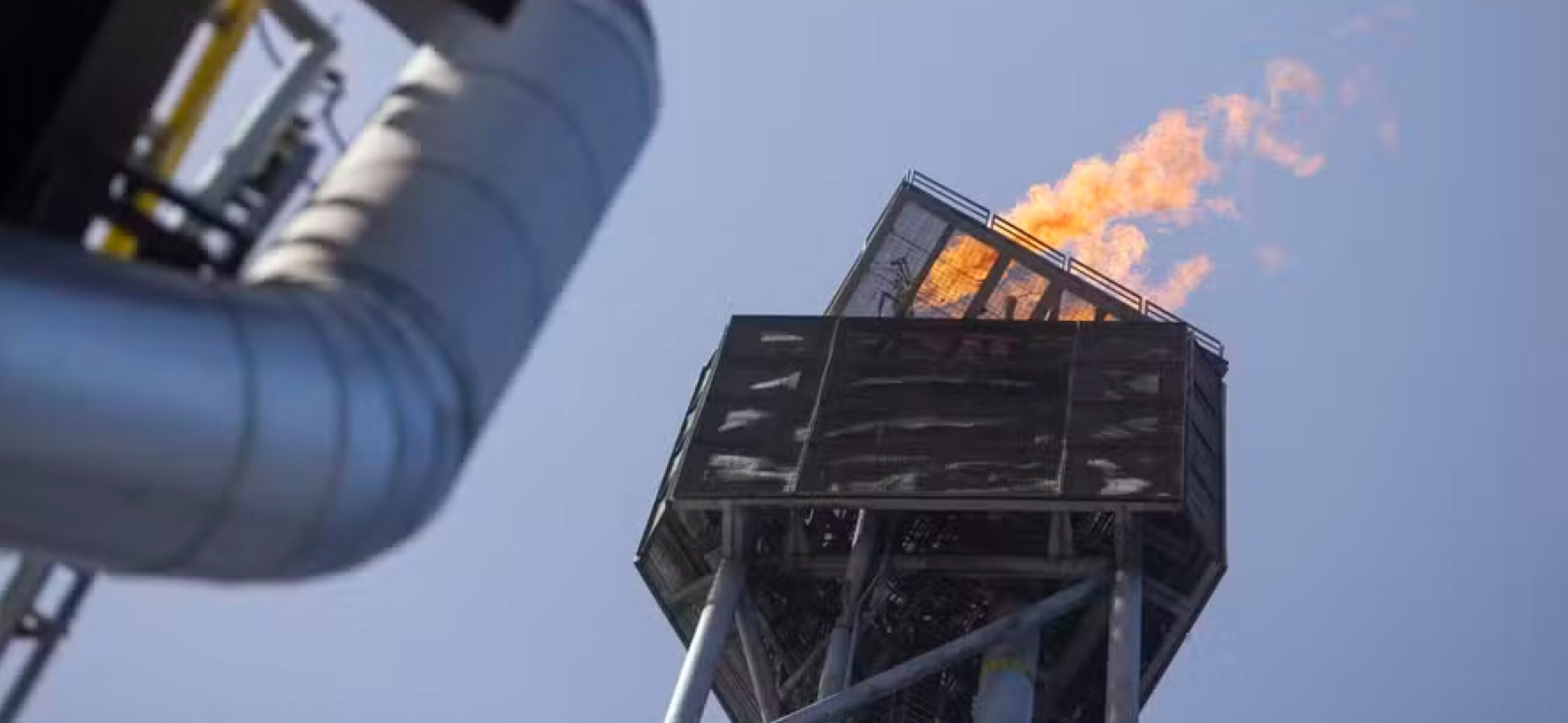
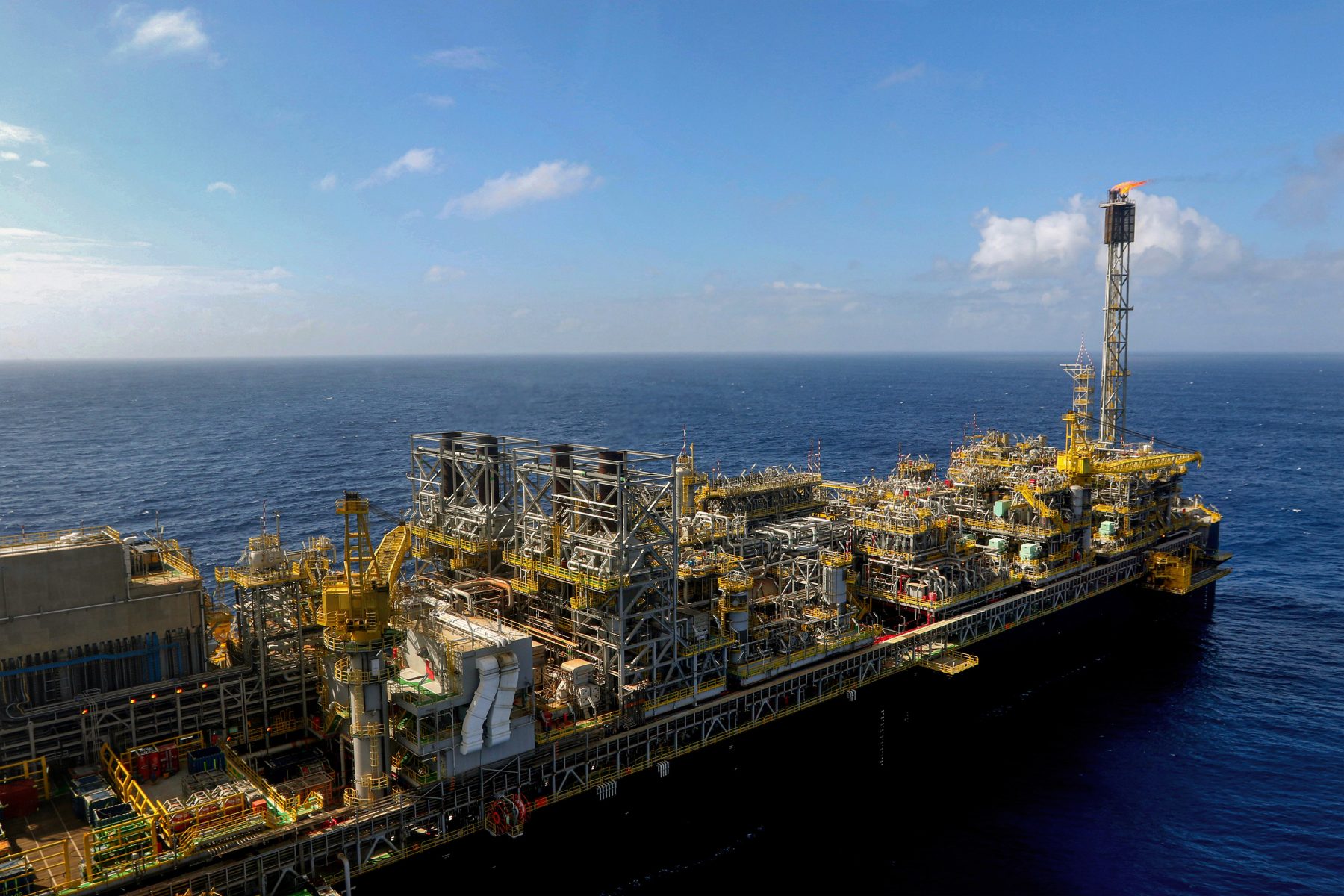
Brazil’s largest inland fossil fuel fields lie deep in the Amazon forest and have been active since the 1980s, whereas its offshore Amazon reserves are still untapped.
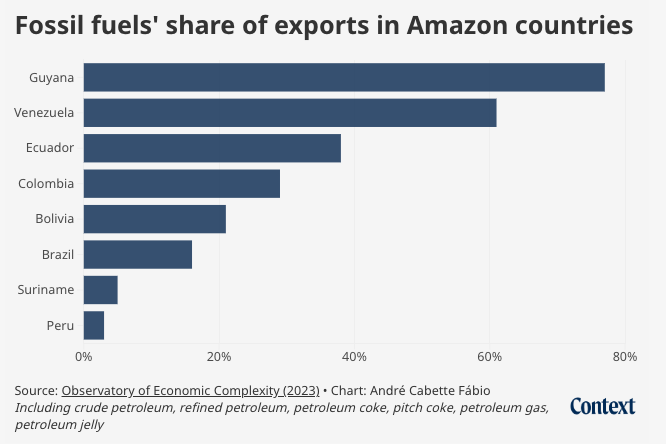
For most Amazon countries, oil and gas are a crucial part of their exports – 77% for Guyana and 61% for Venezuela, for example, according to 2023 data from the Observatory of Economic Complexity, an online platform that gathers data on international trade.
In Brazil, the largest economy in South America, oil and natural gas made up 16% of exports in that year, second only to soybeans.
What are the impacts of fossil drilling in the Amazon?
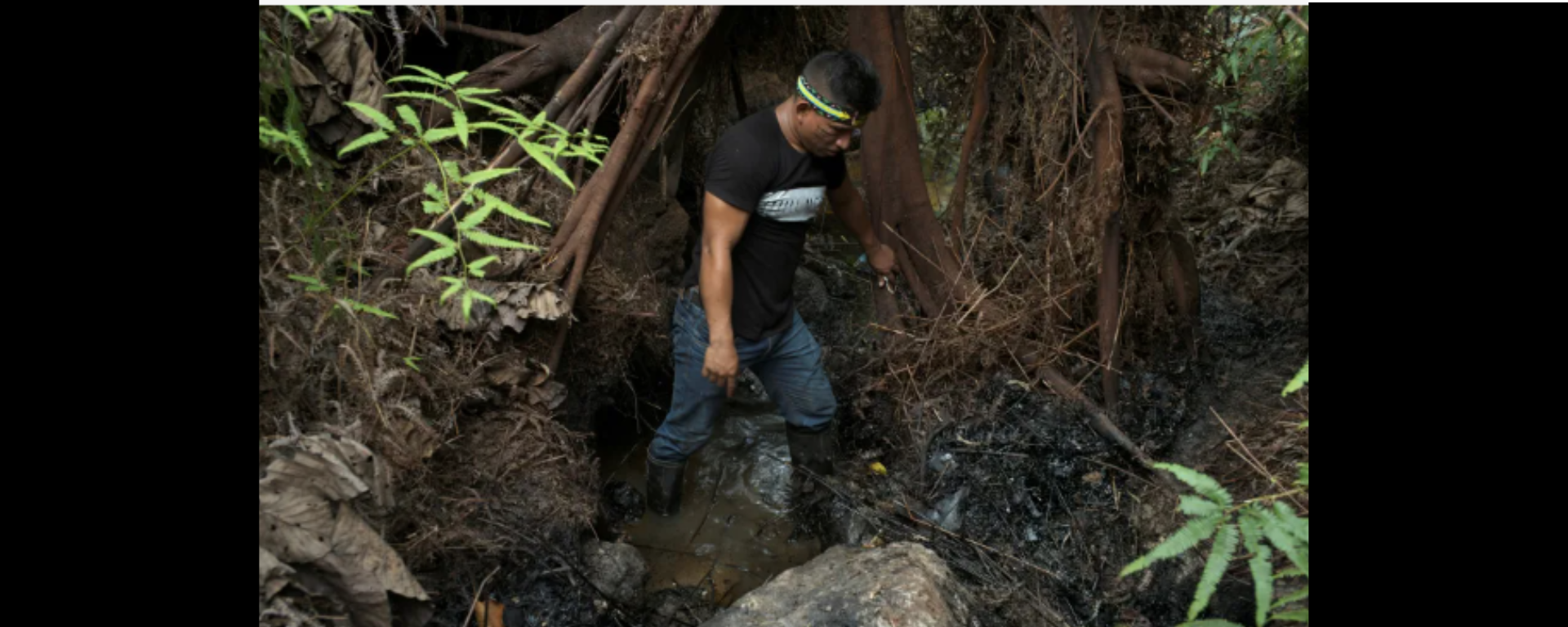
In Peru, Colombia and Ecuador, oil spills from old, deteriorated pipelines are a longstanding issue, contaminating water resources, harming ecosystems and leading to health issues from toxic chemicals.
According to a 2020 report from international NGO Oxfam, there were 474 oil spills in the Peruvian Amazon between 2000 and 2019.
In Ecuador, a 2024 report from environmental advocacy group Stand.earth and the Coordinating Body of Indigenous Organizations of the Amazon Basin (COICA) identified more than 4,600 oil spills and contamination between 2006 and 2022.
The building of infrastructure, such as roads and pipelines, which attracts outsiders and fragments the forest as well as stirs up corruption in state-controlled companies, add to the impact, Stand.earth said.
Where is extraction off limits?
In a landmark 2023 Ecuador referendum, voters halted production by state oil company Petroecuador in the Yasuni Amazon reserve that had started in 2016.
Rules across Amazon countries also restrict drilling for fossil fuels and other minerals in territories with high degrees of environmental protection.
In Brazil, home to about 60% of the Amazon rainforest, fossil fuel drilling and mining are prohibited in Indigenous lands.
The country’s Congress and the Supreme Court have, however, been discussing an agreement that could open up that land for such activities, going against the will of the Indigenous movement.
Which institutions are financing drilling in the Amazon?
According to Stand.earth’s 2024 report, the five top financiers of Amazon oil and gas drilling are Citibank, JPMorgan Chase, Itaú Unibanco, Santander and Bank of America.
Among them, the banks invested more than $20 billion in oil and gas projects in the Amazon in the last 20 years, 47% of the total amount detected by the report.
The document recommended that banks rule out financing any transactions in the oil and gas sector in the Amazon region.
(Reporting by Andre Cabette Fabio; Editing by Ellen Wulfhorst)
Context is powered by the Thomson Reuters Foundation Newsroom.
Our Standards: Thomson Reuters Trust Principles
Picture: A community leader, shows oil contamination inside Block 192, a dormant Amazon oil field near Nuevo Andoas, Peru February 21, 2022. REUTERS/Alessandro Cinque












